Applications of MR Contrast Agents
> research > Applications of MR Contrast Agents
Our group has researched for new MRI contrast agent from synthesis to characterization using physiological, chemical, biological study as below
1. Synthesis
The whole ligands and its complexes were synthesized by the literature with some modification as illustrated below scheme 1 [J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 143вАУ152]. All compounds were confirmed by microanalysis and spectroscopic techniques such as 1H NMR, Elemental analysis, HRFAB mass spectrometry. Our lab was registered in laboratory safety management system at Kyungpook National University and well equipped with instrument for safety and chemical synthesis.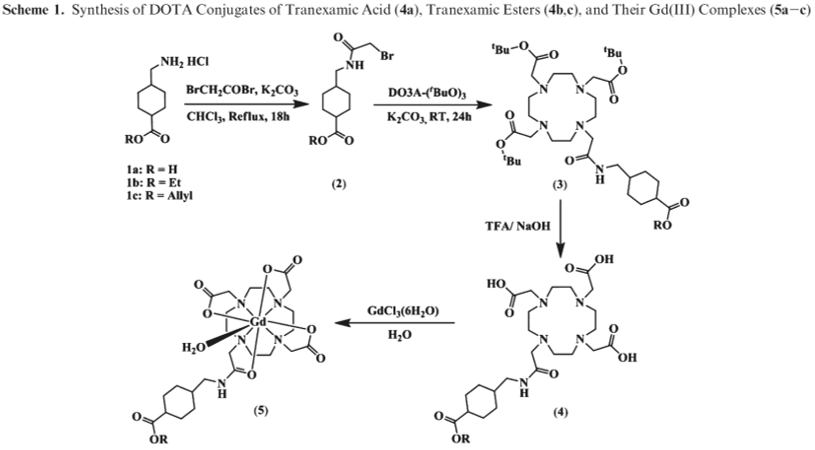
Scheme1. Synthesis of DOTA conjagates of tranexamic acid, tranexamic ester, and their Gd(III) complexes.
2. Relaxivity
Relaxivity indicates the efficiency of MR contrast agent which catalytically shortening the relaxation rate as a function of concentration. The magnetic resonance (MR) images were acquired at the number of varying parameter within different concentration. Relaxivity value was computed by measured relaxation rate (from inverse of relaxation time) value in 1mM.
Figure1. MRI acquisitions at 1.5T of the phantom samples used for relaxivity calculation (left) and relaxation rate of GdL1 as a function of concentration.
3. in vivo MRstudy
The MR study was performed before and after administration using a 1.5T MR unit. It was scanned for several hours to observe biodistribution and excretion pathway. After administration, it was circulated whole body through the vessel with contrast enhancement, (in some cases, organ specific) and finally excreted out from the body. This study helps us know which biological function the newly designed contrast agent has.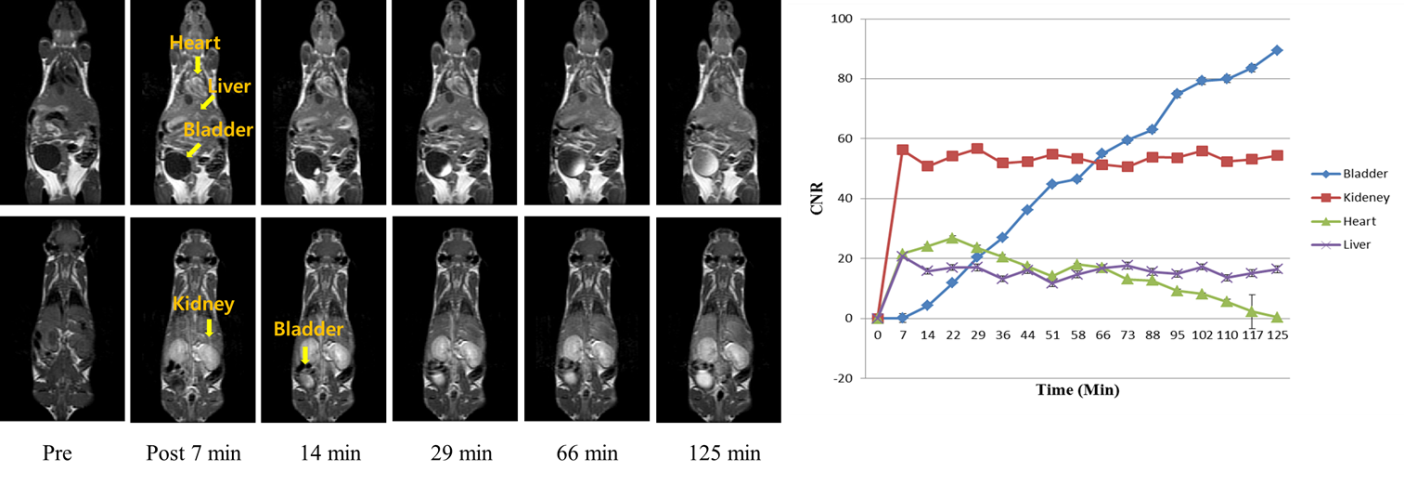
Figure 2. Coronal T1-weighted whole body images of 6-week male ICR mice with GdL, a dosage of 0.1mmol/kg and its CNR profile.
4. kinetic stability study
The Gd complexes can be kinetically labile to suffer from transmetallation by endogenous ions like Cu(II), Ca(II), Zn(II) in the human body. The kinetic stability of Gd complex was focused especially in the presence of Zn(II) ions, because of its high affinity toward common gadolinium chelates, DTPA and DOTA, thereby kicking the toxic Gd(III) ions out much more. When the transmetallation of the Gd complexes was occurred in phosphate-buffered solution with the presence of ZnCl2, the expelled Gd(III) ions would form Gd2(PO4)3, thereby decreasing relaxation rate due to loss of paramagnetic properties. The relative value of R1P at any time t, R1P(t)/R1P(0), is therefore a good estimate of the extent of transmetallation. The evolution of R1P(t)/R1P(0) was shown in below [J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 143вАУ152]
Figure 3. The evolution of R1P(t)/R1P(0) of 5a-c,6 and commercial contrast agents.
In addition to these studies, various studies can be performed according to the function and purpose of newly designed contrast agent as illustrated in our publications.
к≤љлґБлМАнХЩкµР мГЭм≤імЭШнХЩмЮРкЄ∞к≥µл™ЕмШБмГБмЧ∞кµђмЛ§(BMRLab) лґДмЮРмШБмГБмЭШнХЩнМАмЭА мХДлЮШмЩА к∞ЩмЭА мГЭм≤і, нЩФнХЩ, мГЭлђЉнХЩм†Б мЧ∞кµђл•Љ нЖµнХі нХ©мД±мЧРмДЬ нКємД± лґДмДЭмЧР мЭіл•ікЄ∞кєМмІА мГИл°ЬмЪі MRIм°∞мШБм¶Эк∞Хм†Ь лУ±мЭШ лґДмЮРмШБмГБм†Ьм†Ь л∞П мЭШмХљм†Ьм†Ь(нХ≠мХФм†Ь лУ±)мЧР лМАнХЬ мЧ∞кµђл•Љ нХШк≥† мЮИмКµлЛИлЛ§.
1. нХ©мД±
м†Дм≤і л¶ђк∞ДлУЬ л∞П кЈЄ м∞©лђЉмЭА лЕЉлђЄмЭД м∞Єк≥†нХШмЧђ мХДлЮШмЭШ лПДмЛЭ1мЧР мШИмЛЬ лРЬ л∞ФмЩА к∞ЩмЭі нХ©мД±лР©лЛИлЛ§. [J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 143-152]. л™®лУ† нЩФнХ©лђЉмЭА 1H NMR, 13C NMR, мЫРмЖМ лґДмДЭ, Anal-HPLC, LC/MS, High resolution FAB/MS мЩА к∞ЩмЭА лѓЄмДЄмИШм§АмЭШ лґДмДЭ л∞П лґДкіС кЄ∞мИ†мЧР мЭШнХі нЩХмЭЄлР©лЛИлЛ§.
лПДмЛЭ1. нКЄлЭЉлД•мВЉмВ∞, нКЄлЭЉлД•мВЉмВ∞ мЧРмК§нЕМл•імЩА к≤∞нХ©нХЬ к∞АлПМл¶ђлКД м∞©лђЉмЭШ нХ©мД±
2. мЮРкЄ∞мЭімЩДлПД(relaxivity) мЄ°м†Х
мЮРкЄ∞мЭімЩДлПДлКФ мЮРкЄ∞мЭімЩДмЬ®мЭД лЛ®мґХмЛЬнВ§лКФ мЧ≠нХ†мЭД нХШлКФ MRм°∞мШБм¶Эк∞Хм†ЬмЭШ нЪ®мЬ®мЭД лВШнГАлГЕлЛИлЛ§. лЛ§мЦСнХЬ лЖНлПДмЩА лЛ§мЦСнХЬ лІ§к∞Ь л≥АмИШ м°∞к±імЧРмДЬ мЄ°м†Х лРЬ мЮРкЄ∞мЭімЩДмЬ®л°ЬлґАнД∞ к≥ДмВ∞мЭД нЖµнХі мЮРкЄ∞мЭімЩДлПДл•Љ мЦїмЭД мИШ мЮИмКµлЛИлЛ§.
кЈЄл¶Љ1. мЮРкЄ∞ мЭімЩДлПД мЄ°м†ХмЭД мЬДнХЬ мГШнФМмЭШ мЮРкЄ∞к≥µл™ЕмШБмГБ (1.5 T) к≥Љ лЖНлПДмЧР лФ∞л•Є нХ®мИШл°Ь лВШнГАлВЄ мЮРкЄ∞мЭімЩДмЬ® кЈЄлЮШнФД
3. мГЭм≤і лВі мЮРкЄ∞к≥µл™ЕмШБмГБ мЛ§нЧШ (In-vivo MR)
мГЭм≤і лВі мЮРкЄ∞к≥µл™ЕмШБмГБ(MRI) м°∞мШБм¶Эк∞Х мЧ∞кµђлКФ 1.5T, 3T, 4.7T, 9.4T MRI мЮ•мєШл•Љ мВђмЪ©нХШмЧђ мХљлђЉмЭШ нИђмЧђ м†ДнЫДмЧР мИШнЦЙлР©лЛИлЛ§. нХ©мД±нХЬ м°∞мШБм¶Эк∞Хм†ЬмЭШ мГЭм≤і лґДнПђ л∞П л∞∞мД§ к≤љл°Ьл•Љ кіАм∞∞нХШкЄ∞ мЬДнХі мХљлђЉ нИђмЧђ нЫД мХљ 3мЛЬк∞Д лПЩмХИ мШБмГБмЭД мЦїмКµлЛИлЛ§. нИђмЧђ нЫД, мХљлђЉмЭі нШИкіАмЭД нЖµнХі м†ДмЛ†мЭД мИЬнЩШнХШл©∞ мШБмГБмЭШ лМАм°∞лПДл•Љ нЦ•мГБмЛЬнВ® нЫД (м°∞мШБм¶Эк∞Хм†Ь нКємД±мЧР лФ∞лЭЉ мЮ•кЄ∞ нКємЭімД±мЭі мЮИмЭМ) м≤імЩЄл°Ь л∞∞мґЬлРШлКФ к≤ГмЭі мЭЉл∞Шм†БмЮЕлЛИлЛ§. мЭі мЧ∞кµђлКФ мГИл°Ь мД§к≥ДлРЬ м°∞мШБм†Ьк∞А к∞АмІАк≥† мЮИлКФ мГЭлђЉнХЩм†Б кЄ∞лК•мЭД нММмХЕнХШлКФ лН∞ лПДмЫАмЭі лР©лЛИлЛ§.

кЈЄл¶Љ 2. 6м£Љл†є ICR mouseмЭШ кіАмГБл©і(Coronal) мЮРкЄ∞к≥µл™ЕмШБмГБк≥Љ CNR(Contrast to noise ratio) кЈЄлЮШнФД
*м°∞мШБм¶Эк∞Хм†Ь нИђмЧђлЯЙ: 0.1 mmol/kg
4. мЖНлПДл°†м†Б мХИм†ХмД± мЧ∞кµђ
к∞АлПМл¶ђлКД м∞©лђЉмЭА мЭЄм≤і лВімЭШ Cu(II), Ca(II), Zn(II)мЩА к∞ЩмЭА лВімЮђмД± мЭімШ®к≥ЉмЭШ кЄИмЖНкµРнЩШ мЮСмЪ©(transmetallation)мЬЉл°Ь мЭЄнХі, л∞∞мЬДк≤∞нХ©лРЬ к∞АлПМл¶ђлКДмЭі м≤ілВімЧРмДЬ лґИмХИм†Х нХ† мИШ мЮИмКµлЛИлЛ§. к∞АлПМл¶ђлКД м∞©лђЉмЭШ мЖНлПДл°†м†Б мХИм†ХмД±мЭА нКєнЮИ Zn(II) мЭімШ®мЧР міИм†РмЭД лІЮмґФмЦі мІДнЦЙ лРШлКФлН∞, мЭілКФ Zn(II) мЭімШ®мЭі мЭЉл∞Шм†БмЬЉл°Ь мВђмЪ©лРШлКФ к∞АлПМл¶ђлКД нВђл†ИмЭінКЄмЭЄ DTPAмЩА DOTAмЧР лЖТмЭА мєЬнЩФ놕мЭД к∞Ам†Є лПЕмД±мЭі к∞ХнХЬ к∞АлПМл¶ђлКД мЭімШ®мЭД лНФ лІОмЭі мГЭмД±нХШлКФ к≤∞к≥Љл•Љ к∞Ам†ЄмШ§кЄ∞ лХМлђЄмЮЕлЛИлЛ§. ZnCl2л•Љ лД£мЦім§А мЭЄмВ∞мЧЉ мЩДмґ© мЪ©мХ°мЧРмДЬ к∞АлПМл¶ђлКД м∞©лђЉмЭШ кЄИмЖНкµРнЩШмЮСмЪ©мЭі мЭЉмЦі лВђмЭД лХМ, л∞©мґЬ лРЬ к∞АлПМл¶ђлКД мЭімШ®мЭА Gd2(PO4)3л•Љ нШХмД±нХШл©імДЬ мГБмЮРмД±мЭД мЮГк≤М лРШмЦі мЮРкЄ∞мЭімЩДмЬ®мЭі к∞РмЖМнХШк≤М лР©лЛИлЛ§. лФ∞лЭЉмДЬ мЮДмЭШмЭШ мЛЬк∞Д tмЧРмДЬмЭШ мГБлМАм†БмЭЄ к∞Т, R(t)/R(0)мЭД нЖµнХі кЄИмЖНкµРнЩШ мЮСмЪ© м†ХлПДл•Љ мШИмЄ°нХ† мИШ мЮИмКµлЛИлЛ§. [J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 143-152]
кЈЄл¶Љ 3. м∞©лђЉ 5a-c, 6к≥Љ мГБмЪ© м°∞мШБм†ЬмЭШ R(t)/R(0) л≥АнЩФ
мЭілЯђнХЬ мЧ∞кµђ мЩЄмЧР мГИл°Ь мД§к≥ДлРЬ м°∞мШБм¶Эк∞Хм†ЬмЭШ кЄ∞лК•к≥Љ л™©м†БмЧР лФ∞лЭЉ лЛ§мЦСнХЬ мЧ∞кµђк∞А мИШнЦЙлР† мИШ мЮИмКµлЛИлЛ§.(мґЬнМР лРЬ лЕЉлђЄ м∞Єм°∞)
601, 515-3, Hakjeong-dong, Buk-gu, Daegu 702-911, Republic of KOREA | Tel : +82-53-950-4128, 4129 | e-mail : ychang@knu.ac.kr
Copyright(c) 2016 Kyungpook National University School of Medicine BMR lab. All rights reserved.


